AI Agents vs. LLMs vs. AI Assistants: Choosing the Right Tool for the Task
Discover how each AI type excels in specific roles, from generating content to managing complex operations autonomously.
An Apple study exposes deep cracks in LLMs’ “reasoning” capabilities.
Tech giants and pioneers are working to transform the landscape of AI as Artificial Intelligence (AI) is integrated everywhere today, from the smartphone in your pocket to advanced software running entire factories.
Yet as AI advances, the terminology around it is also evolving, and new terms like “AI Agents,” “Large Language Models (LLMs),” and “AI Assistants” are used to describe various types of technology.
These terms, while similar, actually refer to very different kinds of AI functionality, and understanding the distinctions between them can help us better grasp the capabilities and potential applications of each. In this blog, we’ll dive into the meaning of AI Agents, LLMs, and AI Assistants, comparing their purposes, functionality, and real-world use cases. By the end, you’ll have a clear sense of where each type of AI fits into our daily lives and how they are shaping the future.
Large Language Models (LLMs): The Brains Behind Text-Based AI
LLMs, or Large Language Models, represent one of the most groundbreaking advancements in artificial intelligence in recent years. These models are trained on massive datasets of text—anything from books to web pages, articles, and other forms of human-written content. The objective? To understand and generate text that’s contextually relevant, grammatically correct, and even nuanced in tone and style.
Key Characteristics of LLMs
How LLMs Work
When you interact with an LLM, you’re essentially engaging with a system that “understands” language in a mathematical and statistical sense. For instance, when you type a question, the LLM breaks down your query, predicts what an answer might look like, and generates a response accordingly. It uses patterns it has learned from its training data to give a response that feels both natural and contextually appropriate.
Applications of LLMs
Customer Support: Automated chat support, where the LLM provides accurate responses to common questions.
Content Generation: Writing blog posts, articles, emails, and even code.
Language Translation: Translating between languages while preserving meaning and tone.
Education: Assisting with homework, essay writing, and other learning tasks.
Despite their sophistication, LLMs are limited to generating and processing text. They don’t “do” anything beyond that unless paired with other systems or APIs that enable actions like ordering food or setting reminders.
AI Agents: Autonomous Entities with Goals and Actions
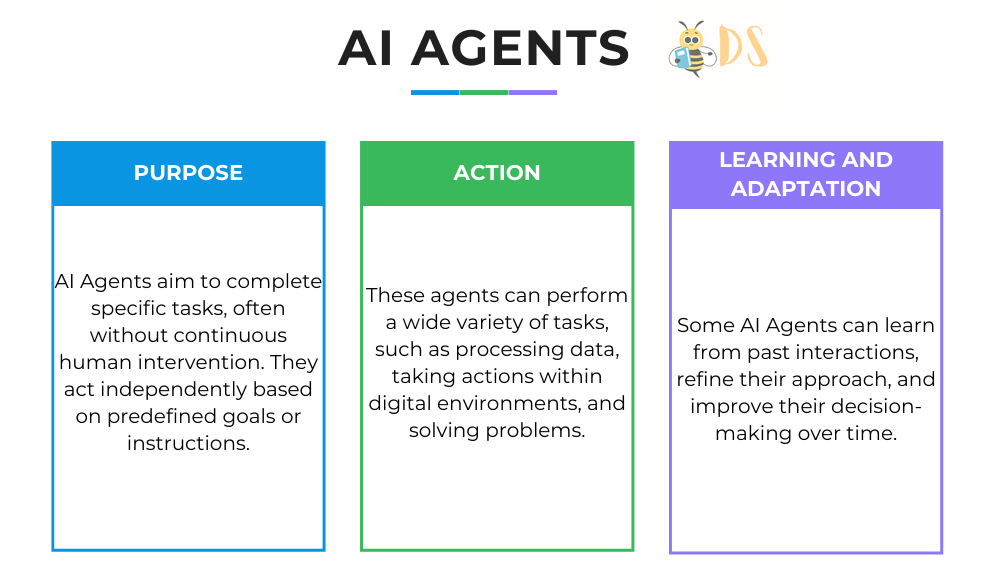
AI Agents take the functionality of LLMs a step further. Rather than simply understanding and generating text, AI Agents are designed to perform specific tasks autonomously based on set objectives. These agents can make decisions, carry out actions, and even interact with other systems or people in real-time. Think of an AI Agent as a specialized, autonomous “doer” rather than just a “thinker.”
Key Characteristics of AI Agents
How AI Agents Work
AI Agents function by combining an LLM’s understanding with additional systems that enable real-world interactions. They are often given an objective and operate within certain constraints, following “rules” or programmed decision-making pathways. For example, an AI Agent for customer service may autonomously respond to queries, recognize when it needs to escalate a situation, and transfer a customer to a human representative if necessary.
An emerging example is OpenAI’s recent development of autonomous AI Agents, which are designed to tackle complex, multifaceted tasks like project management, where they interact with multiple people or systems to achieve a larger goal.
Applications of AI Agents
Personal Finance: Managing budgets, investments, or even paying bills on a user’s behalf.
Project Management: Keeping teams on track, assigning tasks, and managing deadlines autonomously.
Supply Chain Optimization: Predicting demand, ordering supplies, and managing inventory.
Gaming: Creating non-player characters (NPCs) that adapt to player behavior, providing dynamic and engaging experiences.
AI Agents hold enormous potential, as they combine data-driven decision-making with action-based execution, making them much more versatile and useful in real-world applications compared to LLMs alone.
AI Assistants: Your Digital Helper with a Limited Scope
Most people are familiar with AI assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant. These digital helpers represent the middle ground between LLMs and AI Agents, offering users a simple interface to get things done without heavy lifting. AI Assistants are designed to be user-friendly and provide a natural, conversational interface for interacting with technology.
Key Characteristics of AI Assistants
How AI Assistants Work
AI Assistants operate using a combination of natural language processing (often powered by LLMs) and rule-based actions. They understand simple commands and carry out straightforward tasks but are limited to a predefined range of capabilities. For instance, you can ask Google Assistant to set a timer, but it won’t autonomously schedule your calendar based on your work priorities—something an AI Agent might be able to do.
Applications of AI Assistants
Smart Home Control: Managing connected devices like lights, thermostats, and security systems.
Hands-Free Help: Offering drivers or busy users the convenience of voice-activated commands.
Scheduling and Reminders: Setting reminders, alarms, and calendar events.
Information Retrieval: Providing answers to basic questions, weather updates, and simple navigation.
AI Assistants are often limited by their lack of true autonomy and learning capabilities, making them best suited for routine, predictable tasks.
Key Differences Between LLMs, AI Agents, and AI Assistants
Why It Matters: The Future of AI in Everyday Life
The distinction between LLMs, AI Agents, and AI Assistants is critical as we envision the future of AI. Each has unique strengths and potential, and understanding these can help businesses, developers, and consumers make better use of AI technologies. For instance, a large organization might benefit from deploying AI Agents to automate and manage complex tasks, whereas individual users may find AI Assistants ideal for quick, everyday help.
As AI technology progresses, the lines between these categories may blur, with each type of AI becoming increasingly sophisticated and capable. Already, hybrid models and integrated systems are appearing, combining the text-generating abilities of LLMs, the action-based autonomy of AI Agents, and the user-friendly interface of AI Assistants.
For now, knowing the differences can empower you to leverage the right type of AI for your needs, whether it’s a text-based LLM for content creation, an AI Agent to manage projects, or an AI Assistant to help you stay organized at home. The future of AI is not just about advancing technology but about creating smarter tools that genuinely improve our lives.
If you reached till this point, then i have a high hopes that you enjoyed reading. Please don’t forget to like, share and comment on the post.